Biotin (B7)
Biotin, also known as vitamin B7 or sometimes referred to as vitamin H, is a water-soluble B vitamin that plays a critical role in maintaining the body’s metabolic health. It helps convert food into energy by supporting the activity of enzymes involved in breaking down carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Biotin also contributes to the health of your hair, skin, nails, and nervous system, making it a popular nutrient in beauty and wellness products.
Biotin, also known as vitamin B7 or sometimes referred to as vitamin H, is a water-soluble B vitamin that plays a critical role in maintaining the body’s metabolic health. It helps convert food into energy by supporting the activity of enzymes involved in breaking down carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Biotin also contributes to the health of your hair, skin, nails, and nervous system, making it a popular nutrient in beauty and wellness products.
Functions and Benefits
The main function of biotin is to act as a coenzyme in various metabolic processes, especially in the synthesis of fatty acids, amino acids, and glucose. It is essential for energy metabolism and is involved in gene regulation and cell signaling. Biotin also plays an important role in maintaining healthy hair, skin, and nails, which is why it’s frequently promoted in supplements targeting beauty. Additionally, it supports normal fetal development, making it especially important during pregnancy.
Sources and Requirements
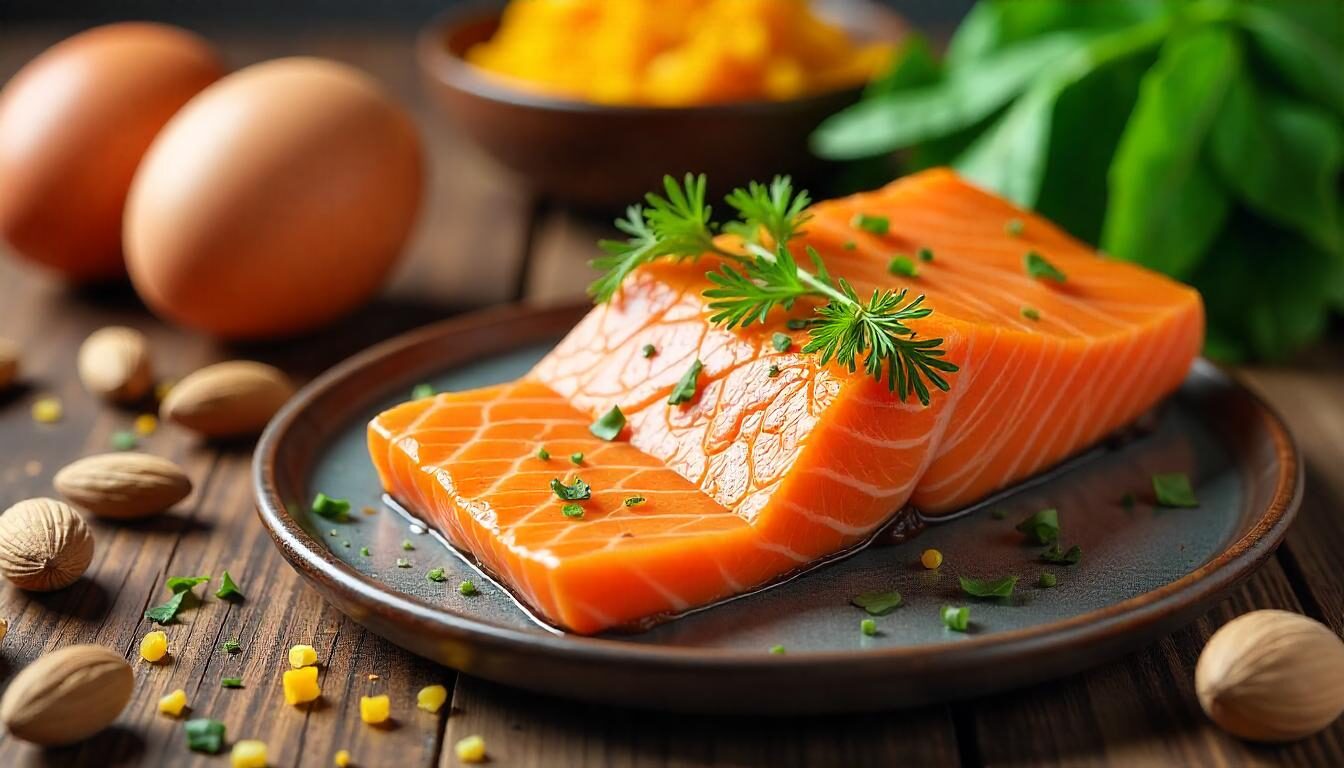
Biotin is naturally found in many foods, making deficiencies rare in healthy individuals with balanced diets. Rich dietary sources include eggs (particularly the yolk), nuts and seeds, legumes, liver, salmon, whole grains, and some vegetables like sweet potatoes, spinach, and broccoli. Biotin is also produced in small amounts by bacteria in the intestines. The adequate intake (AI) level recommended for adults is 30 micrograms per day, and for pregnant individuals, the need slightly increases to about 35 micrograms. Since biotin is water-soluble, excess amounts are typically excreted through urine, reducing the risk of toxicity.

Deficiency and Risk Factors
Biotin deficiency is uncommon, but it can occur in specific situations. People most at risk include those with certain genetic disorders, individuals on long-term anticonvulsant or antibiotic therapy, people who consume large amounts of raw egg whites (which contain avidin, a protein that binds biotin and prevents its absorption), and individuals with alcohol dependence. Symptoms of biotin deficiency may include thinning hair or hair loss, scaly skin rashes (especially around the eyes, nose, and mouth), brittle nails, fatigue, depression, hallucinations, and numbness or tingling in the extremities. In infants, deficiency can lead to developmental delays and skin conditions like seborrheic dermatitis.
Supplementation and Safety
Biotin supplements are often marketed for improving hair growth, strengthening nails, and enhancing skin health. While biotin is widely used in the beauty industry, research supporting its effectiveness in people without deficiency is limited. In those who are deficient, supplementation can significantly improve symptoms. Biotin is considered safe even at high doses, as it has a low risk of toxicity. However, very large doses can interfere with laboratory test results, particularly tests for thyroid hormones, vitamin D, cardiac markers (such as troponin), and even hormone levels, potentially leading to misdiagnosis. For this reason, individuals should inform their healthcare providers if they are taking biotin supplements, especially before undergoing blood tests.
Interactions and Precautions
There are few known drug interactions with biotin, but some medications can lower biotin levels over time. These include anticonvulsants, long-term antibiotics, and isotretinoin (a drug used for acne). People taking these medications may benefit from biotin monitoring or supplementation under medical supervision. It’s important to note that biotin supplements can mask serious medical issues if they affect test results. The FDA has issued warnings regarding high-dose biotin interfering with certain lab tests, emphasizing the need to disclose supplement use to medical professionals.
Conclusion
Biotin (Vitamin B7) is a vital nutrient involved in energy production, metabolic processes, and maintaining healthy hair, skin, and nails. It is naturally available in many common foods, and deficiency is rare in healthy individuals. While supplementation is safe and often used for cosmetic reasons, high doses can interfere with medical tests and should be used with caution. For most people, a balanced diet provides all the biotin the body needs to stay healthy and energized.
Popular Category
- Recipes For Healthy Eating
- Mindset
- Exercises and fitness tips
- Vitamins
- Healthy Lifestyle
See also this
Other posts
Our products